Future research of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants Prepared and conducted by: teacher of biology Maria Oleksandrivna Krayeva. Presentation on the topic “The life of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants” Fragments from the presentation
Presentation on the topic “The life of dicotyledons and monocotyledons” with biology in powerpoint format. The presentation for schoolchildren covers the peculiarities of the life of monocots and dicotyledons. Author of the presentation: Kraeva Maria Oleksandrivna.
Fragments from the presentation
Lesson objectives:
- Get to know the everyday life.
- Discover the peculiarities of the life of monocots and dicotyledons.
- Develop a mindful relationship with natural objects and improve them.
- Form practical knowledge and skills from recognition of the present day and significant present day.
- Practice eco-friendly, environmental protection with the help of the lesson material.
Covering the saplings:
- The organ of reproduction of the baby - the flower - is torn.
- After flowering, the fruit in which the present is found is created.
- It develops in the middle of the fruit, so it is protected (cover).
- The wired system has been well developed, which will ensure the transfer of rivers near the river to the Swede.
Porcelain growths: 1. Plant the organ of reproduction - the flower. 2. After flowering, the fruit in which the present is found is created. 3. The fruit develops in the middle of the fruit, so it is protected (cover). 4. The wiring system has been well developed, which ensures the transfer of rivers near the river to the Swede.





Objectives of the lesson: 1. Learn about everyday life. 2. Discover the peculiarities of the life of monocots and dicotyledons. 3. Develop a mindful way of working with natural objects and upgrading them. 4.Formulate practical knowledge and skills from recognition of the present day and significant present day. 5. Introduce environmentally friendly, environmental protection from the butt material of the lesson.




We've learned that we've got a physical education, we've gotten sick, well, well, well, well! They straightened up, stretched, and now they bent back. We stretch our arms and shoulders, so that it becomes easier for us to sit, so that we can write, read, treasure and not get tired at all. My head was also tired. So let's help her! Right and left, once and twice. Think, think, head. Although the charge is short, we spent a little time.







Keys: 1. The husk is made up of: the husk skin, the germ and the reserve of living speech. 2. Germ – the germ of a new growth. The wine is composed of: germ roots, stems, nirka and cotyledons. 3.Simple doli are thicker than the leaves of the sprout. 4. Roslins that bear one cotyledon at the germ are called monocots - such as wheat, corn, oats, cibul, etc.

Test “I believe - I don’t believe” Nickname, name: “+” ABO “-” 1. Every day there are two cotyledons and endosperm. 2. These plants that have one cotyledon are called dicotyledons. 3. Water enters through the home's outlet. 4. Cover the nasin with bark. 5. The supply of living substances can be in the endosperm. 6. Our aquariums have two cotyledons. 7. Symbols are part of the germ. 8. Reserves of living grapes are found in the stem. 9. Plant monocotyledonous plants with one cotyledon. 10. In our kvass, the heaviest weight comes from the coyote. Inquiry: Rating: Nickname, name: "+" or "-" 1. The natural skin takes on a dry role. 2. Rosliny to the class of dicarots toil one cotyledon. 3. The seed skin is part of the germ 4. The life of the bilobed is composed of the seed skin and the germ 5. In the wheat grain, the reserve life-bearing molecule is located in the endosperm. 6. Place the germ of the caryopsis between two cotyledons. 7. The germ of the spring of the aquarium shoots, mix 2 cotyledons, a root, a stem, a nirka. 8. In today's kvass, lifelong speech is located at the germ. 9. The skin of a grain of wheat can be easily removed. 10. Nasinnya is the germ of a growth. Re-checking task: Evaluation: Having read the propositions, you will see that none of them are confirmed correctly. If it is correct, then put "+", if it is not correct, then put "-" I option II option _ _ + _ _ _ _ _ _

Rating: “5” – no strikes “4” strikes “3” – 3-5 strikes

Questionnaire “Rate the lesson” 1. Did you have a good time? 2.Have you learned anything new? 3. What kind of material was available? 4.Have you come to your senses? 5. What problems have arisen (that have not been resolved)? 6. Your wishes. (the answer “no” - 0 points; the answer “so” - 1 point; on the 5th and 6th of the requested date, the answer is given again)

References: snc6/196329_ _ _362783_ _n.jpghttp://a5.sphotos.ak.fbcdn.net/hphotos-ak-snc6/196329_ _ _362783_ _n.jpg 32.

Lesson objectives:
Methodi ta accepti:
Lesson type:
Lesson instruction:
I. Organizational moment(1 xv)
Updating knowledge (4th century)
Lesson management (1st half)
Budova nasinnya (5th century)
Laboratory robot (15th century)
III. Fastening (10 xv)
IV. Home improvement(3 xv)
V. Lesson bag (1 xv)
Lesson outline:
Organizational moment
Development of new material.
Updating knowledge.
No. 2 - 11 presentations)
White moss.
Storms of seaweed.
Tundra lichen.
Lesson appointment
№ 12 )
№ 13 )
This is their original appearance.
№ 14 - 15 ).
Budova nasinnya
Slidey No. 16 - 17)
Natural skin
Germ -
Sym'yadoli
Endosperm
Monocot trees
Dvodolny
Laboratory robot № 7 :
№ 18 - 23 )
Rib
Micropiles - seeds.
Visnovok:
№ 24 )
№ 25 )
Cereals have skin on top of the grain.
The teacher controls the students' activities. Slidey № 26 - 27 )
Visnovok:
№ 28 )
Secured.
№ 29 - 30)
№ 31 - 34 )
№ 35 )
Home improvement:(Slide No. 36)
Zavdannya-experiment:
Lesson tip:
№ 37 )
cotyledons
(1 chi 2)
stalk
nirka
korynets
endosperm
germ
nasineva
Shkirka
NOW
Forward view:
Budova plant of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants
Lesson objectives:
Lighting. Familiarize scientists with the characteristics of living plants and their significance in nature, and then carry out laboratory research.
Vikhovna. Attach interest to the subject, maintaining diligence and accuracy in the execution of laboratory work and sewing instructions.
Rozvivayucha. Develop the skills of independent initial work, regularly work with a book and work sewing; continue to read, revise, work again. Develop media-communicative abilities of students using the computer.
Methodi ta accepti: explanatory – illustrative, problematic, laboratory robot (preslednytsky)
Lesson type: Development of new material. Lesson-presentation using an additional computer in demo mode. Laboratory robot
Lesson instruction:
A computer for demonstrating a presentation on a lesson topic created by a teacher using PowerPoint.
Installation for Laboratory work: fermented kvass and dry and soggy wheat, collection of sourdough, dissecting heads, magnifiers
tables “Kvasol”, “Grain of wheat”, relief table “Grain”; demonstration material “Wheat”, “Lishchina”, “Sonyashnyk”, “Oak”.
I divided the hour during the lesson:
I. Organizational moment(1 xv)
II. Development of new material
Updating knowledge (4th century)
Lesson management (1st half)
Today, their new look (5 times)
Budova nasinnya (5th century)
Laboratory robot (15th century)
III. Fastening (10 xv)
IV. Home improvement(3 xv)
V. Lesson bag (1 xv)
Lesson outline:
Organizational moment
Development of new material.
Updating knowledge.
(A problem situation is created by the teacher. Children will solve a crossword puzzle for their success. Slideshow No. 2 - 11 presentations)
- Why does the life of a grown-up begin? To get information about the food, solve the crossword puzzle.
White moss.
Storms of seaweed.
Tundra lichen.
Lesson appointment
(Teacher setting up a lesson. Slide № 12 )
- Get to know the everyday life and understand why a little dewdrop grows from it. The natural growth of different plants and the productivity of the stems are maintained. For this purpose we will conduct a laboratory robot, continue to study with a handyman and a working sewer
— Let’s write down the topic for the lesson at Zoshitah.
(Children write down the topic of the lesson from the teacher. Slide № 13 )
This is their original appearance.
(Report from the teacher, demonstration of a collection; children try to guess what kind of plants the teacher is demonstrating. Slide № 14 - 15 ).
— These are divided into shapes, preparations, dimensions, and weight.
Budova nasinnya (Reader's information from Wikoristanny table and diagrams.
Slidey No. 16 - 17)
Natural skinprotects the plant from hanging and mechanical damage.
Germ - This is the beginning of a new growth.
Sym'yadoli - the first leaf germ is stronger.
Endosperm - this is a store of textiles.
Monocot trees- growing plants, in which there are 1 seedlings.
Dvodolny - a plant that has two cotyledon trees looming at the germ.
Laboratory robot № 7 : Vivchennya budov nasіnnya dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants
Budova nasinnya of water-bearing trees
(Setting up the task of the teacher. Children independently design the laboratory work. Worksheet 7 of the laboratory robot is assigned to Fig. 57 on 86 of the assistant.
The teacher controls the students' activities. Slidey № 18 - 23 )
— Vikonite zavdannya zvechku na page 87.
Rib on the inside there is a layer.
Micropiles - seeds.
— At the worker's office, you will see the post 58 on p. 26.
Visnovok: This kvass plant bears a germ from two cotyledons, which is why the plant is a bifurcated plant.
(For the teacher’s instructions, the children draw up the results of the first part of the lab work. The teacher helps to complete the paper correctly. Slide № 24 )
Budova plant of monocots.
(Reader's information from Wikoristan table. Slide № 25 )
Cereals have skin pericarp grows out of the skin of a pine tree. This kind of blanket is called grain.
— Find the place below on page 87 and on p. 88.
(Assignment of the task by the teacher. Children independently continue to complete the laboratory work. Worksheet 5 of the laboratory work follows Fig. 58 on page 87 and the text of the handbook [the first two paragraphs after the laboratory work on page 88].
The teacher controls the students' activities. Slidey № 26 - 27 )
— At the worker's office, you will see the post 59 on p. 26.
Visnovok: A grain of wheat bears an embryo with one cotyledon, which is why the plant is a monocotyledon.
(In response to the teacher’s instructions, the children complete the results of another part of the lab.
Children are trying to earn money on their own. Slide № 28 )
Secured.
1. — Place the “Budova Nasnyna” pattern on the sewing machine and repeat it. (Slide № 29 - 30)
2. — Write in the letters what is indicated in numbers on the little ones on the presentation slide. (Slide № 31 - 34 )
3. — Name the signs of similarity and importance in the future of one and the same aquarius. (Slide № 35 )
(Behind the help of independent work, the teacher sets the stage of their mastering of new material, allowing them to correct themselves. For the needs outside of nutrition, the students are charged again)
Home improvement:§ 18, nutrition after paragraph. Vikonati u robochyu zoshiti zavdannya 60 on p. 27, germinate now for the experiment.(Slide No. 36)
Zavdannya-experiment:
- What can be grown in the minds of the home from the plant that has sprouted, the full-fledged growth, the flowers and dates of fruit?
The boys need to plant the sprouted seeds in the ground near the flower pots and watch for the growths. For this work, the boys are obligated to be careful, meaning that they have to deal with the plants.
Lesson tip: The seedlings are formed from the skin, germ and endosperm. A germ is the beginning of a new growth. The embryo is divided into the root, stem, seed and cotyledons. Our monocots have one cotyledon, and dicotyledons have two. The supply of living substances in different plants can be in the endosperm or in the embryo.
(The teacher’s word about the results of the lesson. Slide № 37 )
cotyledons
(1 chi 2)
stalk
nirka
korynets
endosperm
germ
nasineva
Shkirka

1. Wheat. 2. Chamomile
3. Lupine
4. Konyushina
5. Peas



Kvitkovi
Roslini
Monocots
Dvodolny
corn, tulip
kvass, peas

- 1. Zarodkovy Korinets
- 2. Zarodkova meeting

- Practice at the table carefully.
- Do not be afraid of sudden movements.
- Handle carefully with a prickly tool (spike). Use your fingers to touch the object so as not to prick it.
- Keep the work area neat and do not throw objects away.
- After finishing your work, organize your work place.

Laboratory robot No. 4
Subject : Vivchennya budovi nasinnya kvasoli
Purpose : distinguish the outer and inner waters of the bicarbonate.
Installation of the bathroom Axes: magnifying glass, dissecting head, sourdough sourdough, serveret.

- Take a look at the external appearance of the kvass and see its shape.
- Find the scar and seed.
- While peeling with a dissecting tip, remove the skin from the skin (wet the skin in advance until it becomes sticky).
- Find the germ of today. Vivchit yogo budovu. Look at the parts of the germ: two cotyledons, a germinal root, a stem, a nirka.
- You see, in which part of the fermented kvass there are reserves of life.
- Paint this and sign this part.
- Earn money.

Zarodkov's stem
Zarodkovy Korynets
Shkirka
Sym'yadoli

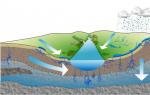
- Water: The embryo of the present day can maintain lifelong speech even if it has a broken appearance.
- Kisen's air: When the seed sprouts, the embryo dies intensively, a constant influx of sourness is required.
- Spare life-long speeches
- Warm: For germination, various types of plants require varying amounts of heat. Roslins that require high temperatures to germinate are called thermophilic, and those that germinate at low temperatures are called cold-tolerant.

1.5-2 mm 2-4 cm 4-5 cm
Friendly Nasnya Middle Nasnyna Great Nasnyna
Poppy Ogirki Garbuz
Turnip Carrot Peas
Tomato Zucchini Salad
Cybula Radish Bobi

Significance of life in nature
Significance of life for people
1. Roslin propagation
- Kharchovy product
2. Rozselennya Roslyn
A. by the wind
B. water
V. Tvarinami
G. Samorozkidannya
A. Grains: wheat, rice, corn, buckwheat, etc.
B. Legumes: peas, kvass, soybeans, beans, etc.
V. Olіyni: dormouse, flax, bavovna, peanut and etc.
G. Tonic: kava, cocoa
D. spices: pepper, cumin, vanilla
2. Material for selection






Thank you for your work.
The presentation was prepared by a teacher of biology at the MBOU ZOSH
r.p. Sura Kazarinova L.V.


- Budova nasinnya class of water-bearing plants
2. Roslini klasa dvodolnih roslin
3. Budova nasinnya class of monocots
4. Roslini class of monocotyledonous roslins
5. The significance of life in life


Laboratory robot
Vivchennya nasinnya digonnogo ta
monocotyledonous plants
Restaurant and food
Result
Take a look at our kvass
Try to remove the skin
Find cotyledons. How many are there?
Peeling with a magnifying glass, find the root, stem and nirka
with leaves
What's in the family?

BUDOVA NASINNYA KLASU DICOLONT ROSLYNS
SHKIRA
GERM
2e
cotyledons
Stem
NIRKA Z LEAVES
KORIN

ROSLINI
WE HAVE
YAKIKH DVI SIM'YADOLI
BE NAMED
BILODINOUS
ROSLINA

Pidsol
casual
Tomato
Garbuz
Yablunya
Morkva
Astra Oak


Restaurant and food
Result
Look at a grain of wheat
Try to remove the skin
Why is the skin not removed?
Break up the grain.
Where are the daily speeches?
Look at the germ

BUDOVA NASINNYA KLASU monocots ROSLYN
endosperm
GERM
SHKIRA
grown up
1
coyote
Stem
NIRKA Z LEAVES
KORIN

ROSLINI IN
NOW
YAKIKH ONE
Nasinnya
BE NAMED
SINGLE CYCLING
ROSLINA

Zhito Oats Millet
Kukurudza Luk Konvaliya Chastukha

Today is the most important achievement in the evolution of Russia.
The filling is made up of a small, slightly shaped
Roslini and stock of living speeches on Persha
hour, the docks of the germ are not simpler.
Nowadays we are stealing this crooked tree from
unfriendly minds.
We will ensure the ability to expand with
for help, water, wind, creatures.

VISNOVOK:
Nasinnya – tse
zarodkovo
Roslina