How do underground waters settle? What is underground water: meaning, characteristics and appearance
Solution of groundwater
Apparently, water is found in the Light Ocean, rivers, lakes, ice fields, and swamps. There may be in the same earth's crust. For the accumulation of water in the earth's crust, two main factors are necessary: a sufficient amount of atmospheric precipitation and the presence of water-permeable and water-draining balls of hydrous rocks in the earth's crust.
From the Bible we learn how Moses gave drink to his people. For this reason, hitting the rock with the club at the bottom of the mountain. And from this place the dzherel began to sound immediately. This example reflects the knowledge of nomadic peoples about underground waters. Because from the bottom of the mountains under the crunchy cover of sand and water, rainwater inevitably collects. It is enough to break this small “scarloupe” in order to obtain water and dissolve the sprague. What are underground waters?
Viznachennya 1
The water that resides in the empty spaces, cracks, and pores of rocks near the upper parts of the earth’s crust is called underground .
It is formed by a natural path, due to the penetration of atmospheric fallout into the soil. The Georgian breeds are subject to discord among authorities. The main thing of her power is the ability to let water go to waste. Breeds that easily pass water include:
- sand,
- gravel,
- pebbles
Tse- water-permeable (water-sensing)) give birth. Trim water of such breeds as:
- clay,
- pishchanik,
- shale,
- granite
Qi breed – water jets.
Water fills the gaps in permeable rocks and creates an aquifer. Aquifers can be found very rarely on different clays. The balls of the Georgian breeds can lie under different coats and prongs. Therefore, the level of contamination of groundwater may change.
Types of groundwater
Behind the drains, underground water flows into
- Verkhivka,
- groundwater,
- interlayers.
Vicennia 2
Verkhovodka - Seasonal water that lies around the lenses on the first surface of the ball of water-resistant rocks.
It does not leak, is kalamutnaya, and during dry periods it evaporates.
Vicenzennya 3
Groundwater – lie like a ball close to the surface and can collapse with a waterproof ball.
Their rhubarb grows slowly due to a large amount of fall. After it gets angry, the water becomes rocky.
Vicenchennya 4
Interlayer waters lie near the aquifers between two water-drinking balls.
Their rhubarb is steady, the water is clean, and flows in Russia along the top of a water-drinking ball.
Viznachennya 5
Interlayer waters that lie in bent balls under constant pressure are called artesian .
Respect 1
If you drill a hole in such a place, the water itself will appear on the surface or flow into the fountain.
Butt 1
Name "artesian" resemble the name of the French proincia Artois , where this water has been used in the reign since ancient times. The world's most pressing artesian spring is found in deep Africa, one of the regions of Algeria. The wine supplies $63$ m of over $4000$ buckets of water for production.
In localities, the release of groundwater to the surface is resolved dzherela .
Groundwater storage
Behind the warehouse, underground water is divided into fresh and mineral.
Viznachennya 6
At great depths, underground water often contains dissolved salts and gases. These waters are called mineral and vikorystvoyutsya for sacramental purposes.
Butt 2
Japan already has a wealth of vibrant mineral minerals. The creatures were the first to brutalize them. The stench knew such jerels for the most obvious wounds. Keeping an eye on the creatures, minerals and hot waters began to vikorize people.
Underground waters vary depending on temperature. They stink cold up to a temperature of $ +20 ° C $. Teplymi call water with a temperature of $+20°C...+37°C$, and thermal - Drive at an even higher temperature.
Heat and thermal waters are found at great depths or in areas of volcanic activity. The stench comes to the surface in the form of hot vents and geysers.
Underground waters give birth to nature’s great work. The stench destroys the Georgian rocks, ruins around the plots of the earth's crust, endures the destruction and vibration of rivers, creates great voids (bees) under the ground, and can cause illnesses.
Ljodoviki
Ice is not water in a solid aggregate. The reason for the transition of water from one camp to another is due to the “perebudova” of Budovo. Just as rare water is more amorphous than the accumulation of water molecules, then “solid” water is more crystalline than water, where the molecules are highly ordered.
Lighting and views of the ice fields
Viznachennya 7
Ljodovik - This is the purchase of fresh ice on land.
Nina ice producers borrow $11$% of land area. High in the mountains, the wind temperature is much lower, lower at the bottom. At its height, it rarely rises above $0°С$. Snow falls there, accumulates and turns into ice. That’s why the tops of the high mountains are covered with snow and ice. The altitude, the stench disappears, is not the same at different latitudes.
Viznachennya 8
The line where more snow falls and less snow can melt is called snow line .
That's the lower limit of the ice-cream settlement.
The ice makers have two areas: tavern and ruhu.
Tavern area to be found more behind the snow line. Here snow accumulates, becomes thicker and turns into ice. Ruhu area moved lower beyond the snow line. Under the influx of force, the heavy ice sheet binds and collapses the surface. There are two types of ice makers. girsky (to cover the peaks and shali gіr) and Pokrivna (ice makers of the Great Society - up to $ 4 $ km, which cover Antarctica and Greenland.
At this time of the geological era, the climate was cold. Therefore, the ice sheets occupied the most important areas of Eurasia and Northern America. The eras of ice were replaced by leagues. The ice producers changed their dimensions or disappeared. It was the worst frost Dnipro Day.
The thickness of permafrost varies from several meters to a kilometer. It is especially widespread in the Eastern Sea region, in the territory of Eurasia and Eastern America. The ice and frozen parts of the mountainous rocks create a solid, soft conglomerate. So it’s easy to rozkopuvati (rozkrivati), dovbati. However, at elevated temperatures and heated soil, ice, water is absorbed by mountainous rocks. They tend to increase and deformation of the layers occurs. This is done in areas of deep permafrost.
Significance of ice fields and aggregation permafrost
- Ice makers are a source of rich fresh ice.
- When collapsing, ice fields cause destruction of the surface and displacement of rock formations.
- Ice producers liven up the Girsky rivers.
- Ice fields and permafrost constitute a potential supply of fresh water on the planet.
Note 3
Nowadays it is important to complicate the government’s activity of people.
Dzherela groundwater
Dzherela groundwater
As a result of the overfilling of the aquifer, water flows onto the surface of the earth near the groundwater drains (dzherels, springs). The deposits appear only after the rainfall and after the fallout has finished falling out and will be quickly exhausted.
Hundreds of millions of liters of water flow on the surface of artesian basins today.
Dzherela is not bordered by surface waters. Recently, hot vents were discovered in the oceans at depths of approximately 2.5 km, most importantly at the mid-ocean ridges. The hot water (more than 300 degrees Celsius) from these waters is rich in minerals and sulphur, which creates a unique ecosystem where unusual and exotic underwater light thrives.
How do the dzherela pretend?
Groundwater reservoirs can flow from different aquifers. Small jerels and keys are sharpened without any influence.
The largest jerelas are formed in karst...
0 0
Underground water supplies
Characteristics of underground water supply reservoirs
Underground waters are the waters found in the upper parts of the earth's crust. Underground waters are created as a result of atmospheric and surface waters percolating into the ground.
These waters practically do not contain suspensions, which are mostly barren, but may also be highly mineralized, containing calcium, magnesium, salt, and manganese in their salt storage. Underground waters are classified both by their characteristics and by the nature of their flow into the chemistry of the aquifer.
Based on clear and complex signs, they can be classified according to the nature of contamination, temperature, chemical composition, and level of mineralization.
Based on the nature of the accumulation, underground water can be divided into perennial water (water from the aeration zone), groundwater and artesian water.
Verkhodka, which lies close to the surface of the earth (1 - 5 m), cannot be a reliable source...
0 0
These are the waters that occur in the Girsky rocks of the earth’s crust. There is more groundwater, and there is less surface water on land – rivers, lakes, and more. The stench is due to atmospheric fallout seeping into the ground. The most important aspect of groundwater is the ability of rock formations to allow water to pass through. There are water-permeable and water-impermeable (water-resistant) rocks.
Water permeability of rocks
Girsky rocks that allow water to pass through are called permeable. These are fluffy porosities (sand, pebbles, gravel) or hard, or cracked rocks (vapnyak, pyshchanik, slate). The larger the parts and pores, the better the water permeability. Girsky breeds that do not allow water to pass through are either waterproof or water-trimming. These are clays or solid rocks that have not cracked. Water from the surface seeps through permeable rocks until it forms waterproof balls on its surface. Here it will be smoothed out, gradually filling up the cracks of the water-permeable pores. Plaster, fill...
0 0
Underground waters
Underground water. Underground rivers, seas and lakes are on the planet.
There are rivers that flow under the earth that rarely appear on the surface of the planet. There are plenty of such rivers all over the world. There are underground rivers, lakes and seas.
How do underground waters settle?
If there are planks of evil over the expanses of the earth, the water will drain the soil. The part evaporates back to the sky, and the solution penetrates deep into the earth. As the mountainous rocks seep through the water, the water plummets downwards. When you reach granite balls, in this place water is collected. The river clears up when the granite ball is under the bank, and the lakes emerge when the streams converge on their path.
Rivers under the ground can flow for hundreds of kilometers. Such a big river flows near the Sahara. Recently, ancient data appeared that, perhaps, an underground river flows under the Amazon.
Sometimes rivers emerge from the ground near a vent, a geyser, or a waterfall. River, what flows under...
0 0
610 Underground waters of Dzherel
Underground waters are the waters of the upper part of the earth’s crust (up to a depth of 12-16 km)
The stench is present in the pores and empty parts of rocks in a rare, solid or vapor-like state. with magmas On the plains composed of sedimentary rocks, you may find balls of varying water permeability. Some of them easily allow water to pass through (sands, gravel, pebbles) and are called permeable, others retain water (clays, crystalline rocks). slates) and are called in the bottom of the ox will be trimmed, fills the gaps between particles of permeable rock and restores the aquifer.
Behind the minds...
0 0
Land waters – rivers, lakes, reservoirs, ice reservoirs, swamps, as well as underground waters (Table 1).
Table 1. Drive sushi
Underground waters
Among land waters, the largest reserves fall on underground waters, underground reserves of which amount to 60 million km3. Underground water can be in a rare, solid, vapor-like state. The stench arises from the soil and rocks of the upper part of the earth's crust.
The ability of rock formations to allow water to pass through depends on the size and number of holes, empty holes, and cracks.
In relation to water, all Girsky breeds are divided into three groups: water-permeable (permeable to water), water-impermeable (suppress water) and water-permeable.
Rozchinnі rocks - potassium and kitchen salt, gypsum, vapnyak. When underground waters break up, large pits, stoves, watering cans, and wells are created in the depths (this phenomenon is called karst).
Water-permeable rocks can be divided into two categories: permeable in all their masses.
0 0
Handbook for 6th grade
Geography
Earth science
§ 41. Underground waters Tell me your fortune
What comes from the water that fell to the ground from the plank? Through some of the Georgian rocks, water will seep more quickly - sand or clay? What are the dzherela (keys)? Why is Dzherel’s water cold for the snail?
How do underground waters settle? Water in the earth's crust occurs in three forms: rare, gas-like and solid. Water and water vapor will fill the spaces between the particles of rocks.
Water in a solid state is crystallized and melts through ice in frozen rocks.
Underground water is the same water found in the Girsky rocks of the earth's crust.
There is more groundwater, and there is less surface water on land – rivers, lakes, and more. The stench is due to atmospheric fallout seeping into the ground. The most important aspect of groundwater is the ability of rock formations to allow water to pass through. There are water-permeable and water-impermeable (water-resistant) rocks.
0 0
Underground waters Underground waters
Water in the depths of the Earth is found in a rare, solid and gas-like state. It either circulates freely through the cracks and pores of rocks and soils, supported by gravity, or is physically and chemically bound to the mineral particles of soils and soils. And from the Georgian breeds.
Underground waters are the waters found in the earth’s crust in all physical states.
Theories and hypotheses about the movement of groundwater
For a long time there were two theories that overlapped each other - this theory of infiltration and the theory of condensation. In the first, it was confirmed that the accumulation of groundwater is the result of the percolation of atmospheric precipitation from the ground and soil, in the other, that the accumulation of groundwater is the water vapor of the atmosphere, which simultaneously sinks into the cold spheres of the earth. noi measles and condenses there.
According to Lebedev (b. 1919), soil and soil are enriched with water as a result of the penetration of atmospheric precipitation, and in...
0 0
Underground waters
All the waters of the earth's crust that are found below the surface of the Earth in rocks in gas-like, rare and solid forms are called underground waters.
Underground waters form part of the hydrosphere – the watery shell of the earth’s cooler. The stench is concentrated in deep waters up to several kilometers deep. For data V.I. Vernandsky, underground water can reach a depth of 60 km due to the fact that water molecules are dissociated by less than 2% at temperatures of 2000o C
The approximate recovery of fresh water reserves at the surface of the Earth to a depth of 16 kilometers gives a value of 400 million cubic kilometers, then. close to 1/3 of the waters of the Light Ocean.
The accumulated knowledge about underground waters, which began in recent times, has accelerated with the emergence of irrigated agriculture. The mystery of expanding dug wells up to several tens of meters was known 2000-3000 thousand BC. in Egypt, Central Asia, India, China. This is also the time when rejoicing began...
0 0
10
The volume of groundwater exceeds the volume of surface water on land. The water in the earth's crust may not only be rare, but also gas-like and look like ice. In the ice, water transforms on frozen rocks.
The reason for the formation of groundwater is the percolation of atmospheric fallout through the rocks of the earth's crust. There are Georgian breeds that allow water to pass through, and those that do not. The first are called water-permeable, and the other are water-resistant.
The rainwater that has fallen on the surface of the earth will seep through the water-permeating balls until the water-drip ball is pressed. As a result, a little more than a water-draining ball, the Girsky rocks become saturated with water and transform into water-bearing rocks.
Rocks that allow water to pass through include sand, pebbles, gravel, vapnyak, sandstone, and shale. This breed is either fluffy or has cracks. Clays and hard rocks that have no cracks are waterproof.
The water flows under the earth as the surface is covered - with more...
0 0
11
CHAPTER 8GEOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF GROUNDWATER
All the water that is found in the pores and cracks of urban areas is carried to the groundwater. The smells are widespread in the earth's crust, and their development is of great importance during the hour of high nutrition: water supply to settlements and industrial enterprises, hydraulic engineering, industrial and civil life, land reclamation iv, resort and sanatorium information too.
The geological activity of groundwater is great. Associated with them are karst processes in rare mountainous rocks, the formation of earthen masses along the slopes of ravines, rivers and seas, the ruination of ancestral bark copalinas and their creation in new places, the removal of various hemispheres and heat from deep zones of the earth. ї measles.
Underground waters, their movement, expansion, migration, clear and complex changes in frequent geological activity are the subject of a special science - hydrogeology, one of the main geology logia.
...0 0
12
Category: Water | and among the children: see the water. | Author-compiler of statistics: Lev Oleksandrovich Debarkader
We will continue to update the “Water” section and the “See Water” section with new types of water. Today the guests have underground waters. Let's talk about what underground waters, stinking stars come from and where they smell. Along the way, we will discuss a number of gastronomical jokes on the topic of groundwater.
Underground water is a collection of names for various deposits of water under the ground. The water under the ground is fresh, even fresh, brackish, salty, over-salted (for example, among the Kriopegi, which we found in the article “Diversity of water in the world”).
Forget all types of groundwater: the stench will grow over the waterproof ball of soil. A waterproof ball of soil is a soil that contains a large amount of clay (does not allow water to pass through) or a soil made of solid rock with a minimum number of cracks.
If you go out onto the street and spread a sheet of polyethylene on the ground, then...
0 0
13
UNDERGROUND WATERS
Water resources are divided according to their respective origins. Those waters that are the most stable in an hour by volume are brought to the highest class.
mu and high quality. With such authorities, the waters of the upper aquifers flow under the ground in the so-called zone of active water exchange. In addition, there is less concern about their contamination with wastewater, domestic and industrial waste. Less valuable water resources are transferred to surface runoff.
The Crimean Peninsula is almost always poor in fresh groundwater, and the stench is of great importance to the people's rule of the region. The formation of the brain is influenced by local, climatic and geological factors. The source of the accumulation of groundwater is the path of percolation (infiltration) of atmospheric precipitation that fell above the given surface, or as a result of the inflow from the side of groundwater that has already settled, or penetration into...
0 0
14
A A A Rozmir text
How to ensure the creation of groundwater
Underground waters are waters that are found under the surface of the earth. Their physical state may be like that, but for the purposes of the ruler's interests, the rarest water reserves can be created. In order to optimally utilize this resource, it is necessary to know how underground waters are created and what types of stench occur.
The distribution of underground water is uneven. The largest spheres, which are formed from high-thickness rocks created by magmatic and metamorphic processes, have little vologies. The main part is located in the surface balls, which are formed during siege warfare.
The water reserves of the upper part are divided into three more balls. The water in the upper ball is most often fresh and can be used for a variety of needs. The middle bowl drains mineralized water. Brines with high mineralization and high content of iodine, bromine and other minerals are less likely to dissolve.
...0 0
15
Types of groundwater
Underground water reservoirs, in their own right, are considered strategic water resources.
Aquifers, moving under the influx of moisture, create unconfined and pressure horizons. The concentration of their waste allows us to classify them into types: soil, soil, interlayer, artesian, mineral.
Volume of underground water
Ground water fills pores, cracks and all spaces between rock particles. We respect the temporary accumulation of dripping waters near the surface waters and are not connected with the lower aquifer.
Ground water - stabilizes the first water-bearing horizon on the surface. This ball experiences fluctuations during different seasons, so that the level increases in the spring-autumn period and decreases in the season.
Interstratal waters, at the same time as ground waters, flow more and more steadily over the course of an hour and lie between two constricted layers.
I remember everything...
0 0
A small part of the Earth’s water reserves are stored in underground pools that flow through the soil and rocks of rocks. Great reserves of groundwater are lakes, which wash away deposits of rocks and soil, making pits.
The importance of unpaved land is great for nature and people. Therefore, the descendants carried out regular hydrological monitoring of this plant as they further believe that there is underground water. The significance, classification and other nutrition will be reviewed in the statistics.
What is underground water?
Underground water is the water that is found in the interspherical spaces of the rocks that lie at the top of the earth's crust. Such water can be presented in any type of aggregate: rare, solid or gas-like. Most often, underground water is equivalent to tons of fluid. Others, beyond the width, did not shave the ice caps that had been preserved from the permafrost period.

Classification
The subterranean waters have been allowed to lie in the soil of their contaminants:
- Ground;
- Ground;
- interlayer;
- mineral;
- artesian.
In addition to overexposed species, underground water is divided into classes that lie near the same ball as the one in which the stench is dissolved:
- The upper level is underground water in fresh water. As a rule, its clay storage is small: from 25 to 350 m.
- The middle horizon is the place where mineral and salt water is deposited at a depth of 50 to 600 meters.
- The lower horizon is a depth of 400 to 3000 meters. Water from the displacement of minerals.
The underground water that grows in the great depths can be young after a lifetime, just a relict that has appeared recently. The remains could have been deposited in underground spheres simultaneously with the soil rocks in which it was “housed.” Or else relict underground water was created in the aggravated permafrost: the ice caps melted - the liquid was accumulated and saved.

Ground water
Ground water is the source that lies at the top of the earth's crust. It is important that it is localized in open spaces between soil particles.
Once we realize that underground water is of the ground type, it becomes obvious that this variety is of the highest quality, and its surface spreading does not remove all minerals and chemicals. elements. Such water is one of the main sources of “life” for rural fields, forests and other agricultural crops.
This variety of soil can always lie horizontally, most often with an outline similar to the relief of the ground. The upper part of the earth's crust does not have a “solid support”, so it is on a suspended position.
The volume of ground water is above average in the spring when there is snow.
Groundwater
The soil variety is a type of water that grows on the deepest depths of the earth’s surface. The depth of the flow of the countryside can be of great show, as it is not dry and empty. In a moderate climate with periodic precipitation, groundwater fallout does not lie so deeply. And if there is too much rain or snow, the soil can become flooded. In some places, this type of water emerges on the surface of the ground and is called a dzherel, a spring or a dzherel.

The soil waters will reappear like the sieges that fell. Many people are confused with the Artesian, but the rest lies deeper.
Surprising amounts of radish can accumulate in one place. As a result of the standing position, swamps, lakes, etc. are created from groundwater.
Interlayer
What is underground water of the interstratal category? These, in essence, are the same aquifers, both groundwater and groundwater, but only the level of their flow is deep, below the two front ones.
A positive feature of interlayer ridges is that the stench is very clean, the fragments lie deeper. In addition, their warehouse so often fluctuates in one constant boundary, and if changes are made, it is insignificant.
Artesian
Artesian waters flow at depths that travel 100 meters and reach 1 km. This variety is important and is the most suitable for living. Therefore, on farm plots, the drilling of drill holes is often practiced as a source of water supply to living tanks.
When the Sverdlov is drilled, artesian water flows like a fountain onto the surface, leaving the fragments as a pressurized variety of groundwater. It lies at the empty ends of the Girsky rocks between the water-bearing layers of the earth's crust.
The reference point for the formation of artesian water is the formation of natural objects on the surface: depressions, flexures, moulds.
Mineral
Minerals are the most abundant and most valuable for human health. The smell of movement instead of various mineral elements, the concentration of which has become.
Mineral waters also have different classifications:
For recognition:
- їdalnya;
- Likuvalna;
- mixed up.
The importance of chemical elements:
- Serkovodnev;
- carbon dioxide;
- slimy;
- yodni;
- bromni.
After the mineralization stage: starting with fresh water and ending with water from the highest concentration.
Classification for recognition
Underground waters are used in everyday life. Their meaning varies:
- nutritious - this is water, which is suitable for drinking either in its natural, unoccupied form, or after purification;
- technical - the center of the world, as it stagnates with various technological, government and industrial considerations.
Classification from chemical warehouse
Rocks that lie very close to the volga are poured into the chemical warehouse of groundwater. The following categories appear:
- Fresh.
- Weakly mineralized.
- Mineralized.
As a rule, the waters that lie very close to the earth's surface are freshwater. And what is more important is the growth of water, especially the mineralization of its warehouse.

How did the underground waters disappear?
A handful of officials are pouring in to illuminate the groundwater.
- Opadi. The litter that fell in the form of planks or snow is clayed with soil to the extent of 20% of the soil volume. The stench forms either the ground or the ground. In addition, these two categories of water take their share of the water cycle in nature.
- Tanenna of ice fields of agatoric permafrost. The underground waters create the entire lake.
- There are also juvenile dens that have settled near the caught magma. A variety of primary waters.
Groundwater monitoring
Monitoring of groundwater is an important requirement, as it allows us to determine its capacity, its volume, its volume, and its presence.
If the acidity of water is determined in a laboratory by examining the obtained sample, then the detection of evidence may depend on the presence of mutual relations:
- First, an assessment of the territory and the presence of transferred groundwater is carried out.
- On the other hand, the temperature indicators of the detected region are simulated.
- Then the radon method comes to a standstill.
- After this, drilling of the base drills is carried out, which is accompanied by core drilling.
- The core is sent for further investigation: this means the century, industry and warehouse.
- A quantity of groundwater will be pumped out of the boreholes in order to determine their characteristics.
- Behind the base drillings, lay down the maps of the location of the core, evaluate their brightness and size.
Groundwater exploration is divided into the following types:
- Front.
- Detailed.
- Operational.

Congestion problems
The problem of groundwater contamination is even relevant today. We can still see the following methods of obstruction:
- Khimichna. This type of obstruction is greater than the widening. Its globality lies in the fact that there is a great number of agricultural and industrial enterprises on Earth, which yield their output in a rare and solid (crystallized) form. These outlets quickly penetrate the water-bearing horizon.
- Biological. Obstructed drains from the hospodar-domestic wastewater treatment plant and faulty sewerage systems are the causes of contamination of groundwater with pathogenic microorganisms.

Classification according to the type of water-saturated soils
They are classified as follows:
- Porovi, like those who lived in the sands;
- cracks, those that will renew the empty shaved rocks and rocks;
- karsts, those that grow in vapnyak rocks or other rocky rocks.
During the process of refining, a water reservoir is formed.
Stock
Underground water is regarded as copalinum, which is natural and takes part in the water cycle in nature. The underground reserves of this variety of bark copalina amount to 60 million km3. However, regardless of those that are not small, the underground waters are strong to the point of congestion, and this is clearly indicated on the basis of the harvested country.
Visnovok
Rivers, lakes, groundwater, ice fields, swamps, seas, oceans - these are the Earth's water reserves, which are interconnected in one way or another. Vologa, which is found in the balls of soil, not only forms an underground pool, but pours water onto the molded surface.
Ground water is available for people's drinking water, and their protection from contamination is one of the main problems of humanity.
Tell me your fortune
- What comes from the water that fell to the ground from the plank? Through some of the Georgian rocks, water will seep more quickly - sand or clay? What are the dzherela (keys)? Why is Dzherel’s water cold for the snail?
How do underground waters settle? Water in the earth's crust occurs in three forms: rare, gas-like and solid. Water and water vapor will fill the spaces between the particles of rocks.
Water in a solid state is crystallized and melts through ice in frozen rocks.
Underground water is the same water found in the Girsky rocks of the earth's crust.
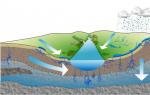
There is more groundwater, and there is less surface water on land – rivers, lakes, and more. The stench is due to atmospheric fallout seeping into the ground. The most important aspect of groundwater is the ability of rock formations to allow water to pass through. There are water-permeable and water-impermeable (water-resistant) rocks (Fig. 142).
Small 142. Water permeability of rocks
Girsky rocks that allow water to pass through are called permeable. These are fluffy porosities (sand, pebbles, gravel) or hard, or cracked rocks (vapnyak, pyshchanik, slate). The larger the parts and pores, the better the water permeability. Girsky breeds that do not allow water to pass through are either waterproof or water-trimming. These are clays or solid rocks that have not cracked.
Water from the surface seeps through permeable rocks until it forms waterproof balls on its surface. Here it will be smoothed out, gradually filling up the cracks of the water-permeable pores. The layers, saturated with water, form water-bearing balls (Fig. 143). The water in them flows down along the heeled surface of a waterproof ball.
What kind of underground waters are there? Through the excavation of pores with varying water permeability in the earth's crust at different depths, there may be a number of aquifers. Fluffy and porous rocks change into water-drip, then again water-permeable and again water-drip. The ground and interstratal underground waters are separated according to the position of the aquifers (div. Fig. 143).

Small 143. Underground waters
The waters of the upper aquifer, drained by the first aquifer, are called groundwater. Interlayer water is distributed between two water-drilling balls. Here, water from the surface drains through the area, where water-bearing spheres come to the surface.
The depth and ability of the ball of groundwater to lie in the geological territory, topography and climate. On the plains with a cold and watery climate, groundwater can reach the very surface, resistant to the pain. Since the climate is hot and dry, groundwater flows to great depths. The depth of groundwater may change with the seasons. In Russia, spring groundwater flows closer to the surface, and inflows further below it.
The porous rocks above the Saharan desert have large reserves of underground fresh water. There are so many of them that the stinks can supply the consumption of all the countries that are spread out on the territory of the desert. However, these waters lie at a depth of 150-200 m above the surface.
Groundwater often comes to the surface, filling the waters (dzherelas, springs) in low relief: river valleys, ravines. Interlayer waters are obtained through specially drilled holes. Sometimes the water flows through the bore like a fountain. Such waters are called artesian (Fig. 144).

Small 144. Artesian waters
Artesian waters appear near the bent balls of the Georgian rocks. The water appears here under great pressure, and it gushes out when the verdure grows.
Not all underground waters are fresh. The actions of them take revenge on a lot of discordant speeches and gases. Such waters are called mineral. At high altitudes near the earth's crust, the temperature rises. That’s why the underground waters become warm and still hot.
Since the earth's crust is composed of easily separated rocks (waps, gypsum, salts), then underground waters are drained from some of the empty, empty, furnaces (Fig. 145). Such a phenomenon of nature, as well as the relief form on the surface, is called karst in the guerilla community.

Small 145. Form karst
Water doesn’t just create karst caves. Vaughn decorates them with rock sculptures. From the speckles that leak out from the stelae of the stoves, like driftwood, stalactites grow down. From the droplets that fall on the bottom of the oven, steps from below grow step by step - stalagmites. These inode forms grow one after another in a single column.
Food and food
- Does water consume so much of the earth's crust?
- Name the types of groundwater.
- What is this dzherelo? Are you trying to pretend?
- Where are karst caves created?
For days I bought the first dance with mineral water. Having read about her work on the labels, I saw an inscription that confirmed that this water was poured from an underground well. I wasn’t really interested in the topic about underground water and their journey. Oz...
How do underground waters settle?
Let's begin with the fact that this is underground water. In its essence, these are the waters that are found in products of the Georgian breeds. In this case, the stench can occur in both rare and solid and gas-like forms.
If we talk about underground waters, we respect their rare type. The stench spreads evenly unevenly. The deepest balls, which are created from particularly thick rocks (which are invariably created by magmatic and metamorphic processes), have virtually no vologies.

The main part of the water lies in the surface balls, the rocks of which are subject to siege warfare.
I will turn around until the underground waters are satisfied. You can get involved in a number of paths.
In this way, the bunts allow the moisture to penetrate from the surface. This process is called “infiltration”. Here the underground waters are enriched not only by the fallout, but also by all the surface water reservoirs. In this case, a lot of water should be deposited in a type of soil.
Another method can be called the precipitation of water vapor, which is generated in the empty wastes of rocks. This is a trivial process.

Types of groundwater
The formation of groundwater can be called a steady and continuous process. Water itself is considered to be an inexhaustible resource.
Ale on okremu riddle merits the appearance of underground waters. There are three main ones:
- Verkhivka. Lie closest to the dirt surface. This type of water is unstable and can easily evaporate when soaked;
- Ground. They are determined by the stability of their replenishment, which is the “main type” of groundwater. Such duties flow into the faceless officials;
- and artesian ones. It stinks “napirni”. They are under pressure and often occupy large areas.

Varto means that the artesian waters themselves will be protected up to the brown copal trees. We all owe it to ourselves to remember the importance of saving ourselves.